What do three years of data on the gender gap in news reporting tell us?
by Shari Graydon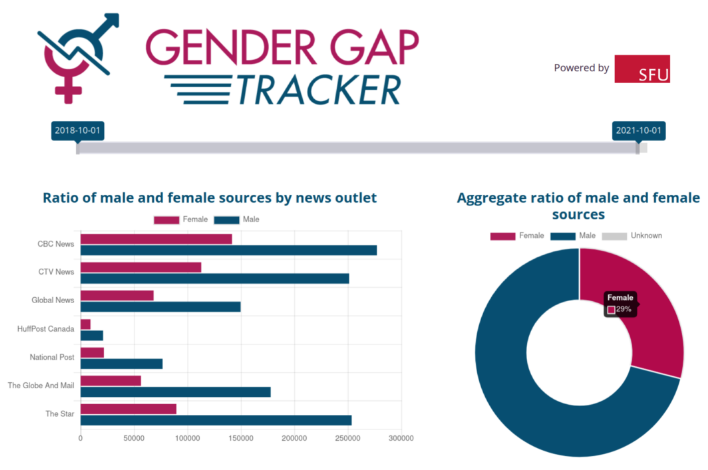 The following op ed, co-authored with Prashanth Rao and Dr. Maite Taboada, appeared on Poynter‘s website on 28 October 2021.
The following op ed, co-authored with Prashanth Rao and Dr. Maite Taboada, appeared on Poynter‘s website on 28 October 2021.
Looking for silver linings in the midst of a pandemic is fraught. But here’s one that journalists need to pay attention to: Since March 2020, news media have devoted a lot more time and space to covering health care, and a lot less time and space to covering hockey fights.
In the process, they’ve featured the perspectives and reflected the realities of a much wider swath of their audience. And for news organizations looking to survive, that’s a useful shift.
The gender gap in news reporting is so longstanding it should be old news. But three years of data and more than 1 million news articles from the most influential English-language news organizations in Canada have highlighted the pitfalls with hard and discouraging data.
In October 2018, we launched the Gender Gap Tracker, a digital analytics research tool that measures in real time the ratio of men and women being quoted in online news. At the time, women’s voices constituted just 27% of the total number of quotes captured. (Because the tool relies on traditional associations of names with genders, it measures gender as a binary, a limitation that denies insight into the continuum of perspectives but remains currently unavoidable, given the technology.)
Over time, however, especially with the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, we saw a recognizable uptick in the proportion of women quoted. Throughout 2021, this has been a sustained trend. On occasion, women’s voices have reached 32% (International Women’s Day, for example), but even during the recent Canadian federal election, in which the major party leaders were all male, the proportion of quotes by women continued to be around 30%.

Percentage of women sources in news stories from October 2018 through October 2021. (Courtesy: Gender Gap Tracker)
Beyond this glimmer of optimism, the Gender Gap Tracker provides useful insights into key issues of relevance to news organizations.
It’s never been a winning business strategy to chronically underrepresent 50% of your potential audience. At a time of shrinking readership and divided attention, there are clear gains to be made from featuring a greater diversity of perspectives. That became even more obvious during the pandemic, given how differently it affected women.
A related problem is what constitutes a “women’s issue.” An analysis by news topic shows that women are consistently quoted more often in so-called “soft news,” on arts and entertainment, health and lifestyle issues. In contrast, men’s voices appear much more often in articles about politics, business and sports.

Monthly gender prominence by topic of sources in news stories from October 2018 through October 2021. (Courtesy: Gender Gap Tracker research dashboard)
This reinforces both sexist stereotypes (women are caregivers; men are leaders) as well as the notion that business is more important than health care. Indeed, the ongoing tension between prioritizing unrestricted reopening of the economy over mask protocols and vaccine passports may be in part a symptom of those entrenched practices.
As the pandemic has shown, relegating to also-ran status the arenas in which women dominate (education, childcare, mental health) can have catastrophic consequences.
Analysis of who is quoted and in what role offers additional insights. Breaking down gender by profession reveals that 60% of the most quoted men and women are elected officials. This not only explains part of the gender gap, since men still dominate politics, but it also paints a more troubling picture about an over-reliance on official sources.
Elected officials often default to canned talking points or partisan interests. Journalists know this and actively seek to challenge the default in interviews. But an additional workaround would be to do a more rigorous job of supplementing government news releases with more alternative sources — including women and other underrepresented populations who are able to speak to the disparate experiences of citizens affected by the policy being proposed.
These insights reflect just a few of those available to extract from the data we amassed over the past three years. In that time, we’ve witnessed both the US 2020 presidential election and two federal elections in Canada. We’ve seen topics change with the seasons and major world events unfold, told through the words of those being quoted.
What has not changed substantially is the gender gap in media reporting. Beyond the obvious need for more equity, leaving that gap unaddressed is a missed opportunity for news organizations.
Prashanth Rao is an applied scientist with a passion for building AI systems with a social impact. Maite Taboada is a computational linguist researching social and traditional media. Shari Graydon is the founder and catalyst of Informed Opinions, an organization dedicated to amplifying women and gender-diverse people’s voices.
